Next generation sequencing (NGS) have enabled an unprecedented view of the phenotypic properties of T cells responding to biologic therapy. NGS tools have enabled us, in collaboration with the Long Lab, to discover that beneficial response to teplizumab therapy, a biologic agent recently approved by the FDA for treatment of type 1 diabetes (T1D), is linked to CD8+ T cell exhaustion.
More recently, we showed that beneficial response to a second T cell-targeting agent, alefacept, was also linked to T cell exhaustion. In this case, we found two distinct exhausted cell populations, one resembling the exhausted two CD8+ T cells found in teplizumab treated subjects, and a second distinct population of NK-like CD8+ T cells.
To probe relationships between exhausted T cell subsets more deeply, we relied on a technique we developed, in collaboration with the Cerosaletti Lab, a novel single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) approach for determining both TCR sequences and full transcriptome phenotypes from individual antigen-specific T cells. We have extended these published procedures to analyze shared ancestry and phenotypic heterogeneity of exhausted T cells associated with beneficial therapeutic response. These experiments have revealed previously unknown shared ancestry between exhausted CD8+ T cells and NK-like CD8+ T cells in peripheral blood.

We are probing molecular mechanisms and causality links between exhausted cell populations and response to therapy.
Featured Publications
-
Partial exhaustion of CD8 T cells and clinical response to teplizumab in new-onset type 1 diabetes.
Sci ImmunolLong SA, Thorpe J, DeBerg HA, Gersuk V, Eddy J, Harris KM, Ehlers M, Herold KC, Nepom GT, Linsley PS -
Exhausted-like CD8+ T cell phenotypes linked to C-peptide preservation in alefacept-treated T1D subjects.
JCI InsightDiggins KE, Serti E, Muir V, Rosasco M, Lu T, Balmas E, Nepom GT, Long SA, Linsley PS -
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Expanded Clones of Islet Antigen-Reactive CD4+ T Cells in Peripheral Blood of Subjects with Type 1 Diabetes.
J ImmunolCerosaletti K, Barahmand-Pour-Whitman F, Yang J, DeBerg HA, Dufort MJ, Murray SA, Israelsson E, Speake C, Gersuk VH, Eddy JA, Reijonen H, Greenbaum CJ, Kwok WW, Wambre E, Prlic M, Gottardo R, Nepom GT, Linsley PS
Additional Research Projects
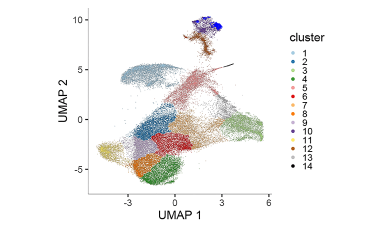
Elucidating immune processes in tumors that affect patient survival and response to therapy
We are investigating whether Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor blockade in cancer treatment promotes the proliferation and survival of T cells specific for self-antigens and tumor antigens that ultimately contribute to adverse immune events or response to therapy.
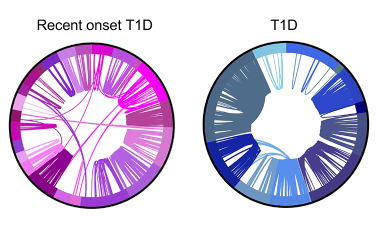
Shared germline-like TCR alpha chains in autoreactive CD4+ T cells in T1D
We found a class of autoreactive T cell receptors (TCRs) that share TCR TRA chains between individuals and that these TCR TRAs are elevated in new-onset T1D patients. We are investigating the role of these public TCRs in autoimmune and anti-infectious agent immune responses.


