The immune “checkpoint” pathway includes the receptor Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). The binding of PD-L1 to PD-1 leads to negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling.
We have found that patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) who have prolonged mechanical ventilation have lower expression of PD-L1 on alveolar macrophages. Further, a serious side effect of pharmaceutical inhibitors of this pathway termed “checkpoint inhibitors” is immune mediated tissue injury such as an ARDS-like pneumonitis. Thus the role of this pathway in modulating immune responses is critical to our understanding of ARDS.
We are studying how PD-L1 affects macrophage function and the effects on T cell responses in primary bronchoalveolar lavage samples from patients with ARDS.

Additional Research Projects
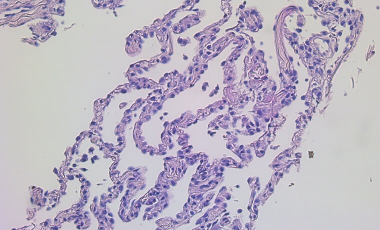
Macrophage Heterogeneity and Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis
We are identifying novel macrophage subsets and investigating how they contribute to acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and interstitial lung disease.
Systems Immunology Profiling of Respiratory Viral Infections in Rheumatoid Arthritis
The lab's study in the Human Immunology Project Consortium (HIPC) is focused on understanding mucosal immune responses in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and how it differs from healthy adults.


